Infection Diagnosis
The first step to responding to a pandemic such as COVID-19 is ‘prompt and accurate diagnosis.’
In infectious diseases, it is important to reduce the spread of contagion through rapid and accurate diagnosis in the early stages of transmission. Molecular diagnostic technology that directly detects the gene of a pathogen uses a method of amplifying the gene of the pathogen and has the highest accuracy among in vitro diagnostic methods.
In addition to the field of respiratory infectious diseases, NGeneBio is expanding its research into various statutory infectious disease that has not yet been introduced into Korea and is developing high-quality diagnostic kits that ensure promptness, accuracy, and comprehensiveness (simultaneous diagnosis of multiple pathogens).
- Real-Time PCR
-
Real-Time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) is a method that can simultaneously detect amplified DNA using fluorescent materials. It can be applied to the DNA of bacteria, viruses, and fungi and used for the diagnosis of infectious diseases.
- NGS
-
A single test can detect hundreds of different pathogenic organisms simultaneously. In additions, full-length genome analysis of pathogens is possible, and known antibiotic resistance mutations and new mutations can be detected. Recently, it is actively used for sequencing COVID-19 mutations.
Identification of respiratory infectious Mycobacteria and commercialization of Mycobacterium tuberculosis multi-drug resistance mutation simultaneous diagnosis kit
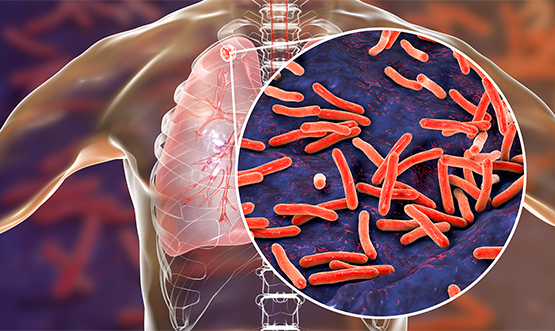
- What is tuberculosis (TB)?
-
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) and is within the most lethal diseases worldwide, killing about 1.6 million people annually. It is known that transmission of tuberculosis bacteria is carried out through airborne infection without a vector, and about 5~10% of infected patients develop active tuberculosis over their lifetime after infection, so early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are necessary to prevent the spread of disease transmission.
- Importance of diagnosing Tuberculosis Drug-Resistance
-
The WHO reported that there were about 450,000 new cases of multidrug-resistance tuberculosis (MDR/RR-TB) in 2021 estimated, of which, about 6% will be extensive drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB).
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR/RR-TB) refers to tuberculosis that is resistant to Isoniazid (INH) and Rifampicin (RIF), which are the first line of anti-tuberculosis drugs in the treatment of tuberculosis, or resistant to RIF alone. Resistance of tuberculosis bacteria to anti-tuberculosis drugs is caused by chromosomal variations, and drug resistance is acquired through major gene mutations related to the major target area or substance of each anti-tuberculosis drug.
For the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, long-term drug treatment including second-line drug is required, and despite such treatment, the treatment success rate is only about 50% worldwide, which is one of the biggest obstacles in the treatment and management.
The usefulness of MTBaccuPanel in tuberculosis diagnosis
The existing tuberculosis confirmation test requires multiple tests including identification of nontuberculous mycobacteria and Mycobacterium tuberculosis, rapid resistance test, culture test and etc. Among them, the Xpert MTB/RIF kit can detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis INFECTION and rifampin resistance. Although it is used in most of clinical laboratories due to high convenience, there is a limitation that rifampin resistance is detected.
When using the MTBaccuPanel that can be save the time and cost since it is possible to analyze all of the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and resistance-related genes. In addition, new mechanisms of resistance can be verified to known variations. As such mechanisms are reflected in the database, it is possible to secure a high level of test accuracy.
Patients suspected of
tuberculosis infection
Sputum collection
-
 Smear Test | Culture Test
Smear Test | Culture Test
Drug susceptibility culture test

Drug-resistant tuberculosis therapy Susceptibility culture test
It is the most accurate, but it takes more
than 6 weeks to confirm the result -
 TB/NTM RT PCR Test
TB/NTM RT PCR Test
Drug Resistance
PCR, LPA Test
Drug-resistant tuberculosis therapy Resistance PCR, LPA Test
Fast, but limited in detecting all
resistance-causing mutations -
 NGS Diagnostic Test
NGS Diagnostic TestTotal confirmation of resistance to
tuberculosis drugs, confirmation of NTM speciesQuickly able to identify all resistance mutations to various anti-tuberculosis drugs at once