NGS Diagnosis
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) is a high molecular technology that mass-produces DNA sequence data and
analyzes them
with bioinformatics algorithms. It is the core technology of precision medicine that offers optimal personalized
treatment
by examining/diagnosing the presence or absence of mutations in genes related to various diseases with a single
test.
Precision Diagnostics
The very beginning of personalized precision medicine is genetic testing.
In the field of precision medicine, which provides customized medical services in reflection of each
patient’s characteristics based on genetic information,
the most actively applied method is the
precision diagnosis of cancer based on NGS technology.
NGS test detects cancer-causing mutations by analyzing the DNA sequence, which is the genetic information of cancer cells. While the existing genetic tests indicates only whether cancer-causing mutations are present or absent, NGS test quantifies mutations in the general mass of tumor and even traces changes of such mutations over time after treatment.
It also detects resistant (e.g.: KRAS) mutations as well as target genes of various targeted therapies (e.g.: EGFR, BRAF, ERBB2, ALK, ROS1, RET, NTRK, etc.). NGS test also makes it possible to measure factors to predict reactions to anticancer immunotherapy such as microsatellite instability (MSI), the total number of mutations (tumor mutation burden), etc.
We develop optimal precision diagnosis solutions through the convergence of biotechnology (BT) and information technology (IT).
BT
- Disease-related genes target panel
- Minimize false-positive and negative
- Performance corresponding with IVD approval standard
- Secure clinical effectiveness

IT
- Data collection
- Analytics algorithm
- Database
- Cloud
- Machine learning
Precision Diagnostics Solutions
- Diagnosis & Prediction
- Personalized disease treatment
- New drug development
- Health management
-
01
BT
Provides a panel optimized for clinical sample testing that accurately and balanced amplifies only disease-related biomarkers and can be applied to trace amounts of samples and FFPE-treated samples. By applying Molecular Barcode technology, false positives are minimized and mutation detection is possible with high sensitivity.
-
02
IT
We build a database by collecting clinical and genomic big data, and provide accurate reading results on disease relevance of genetic mutations discovered through big data analysis and machine learning techniques. We automate complex analysis algorithms and provide them in the form of medical software and provide cloud-based analysis solutions.
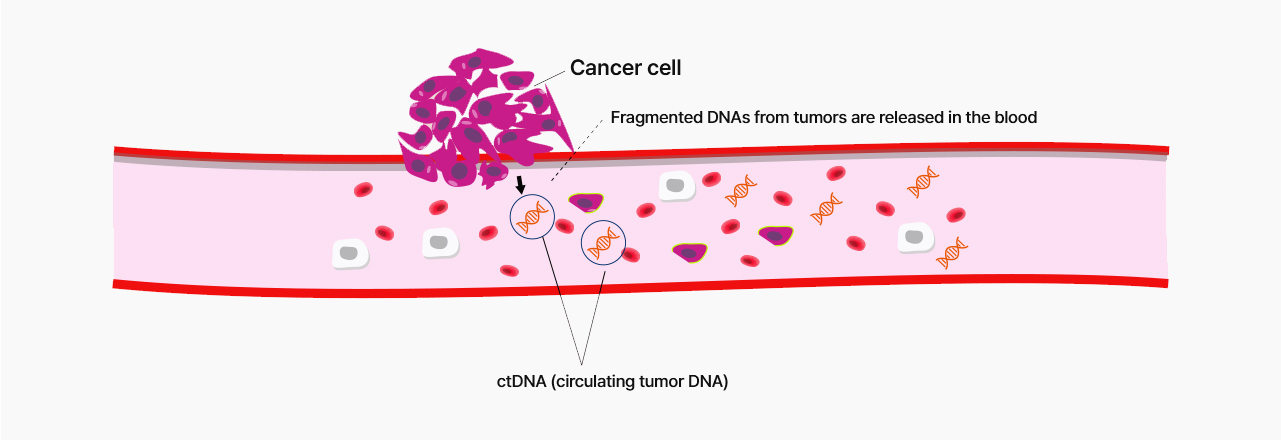
Liquid Biopsy
Available cancer diagnosis, recurrence, and monitoring of chemotherapy based on blood.
‘Liquid biopsy’ is a non-invasive test with body fluids such as blood, urine, and marrow collected
instead of tissues.
Particularly, tumor cells contained in blood or circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) from tumor cells are analyzed
not
only to perform cancer diagnosis but also to monitor minimal residual diseases (MRD) and
cancer recurrences.
- ctDNA to replace tissue biopsy
-
This is useful for patients who do not apply to surgical treatment or biopsy tests, or with only a small number of tissue specimens. It is possible to analyze in reflection of heterogeneity in tumors and to trace changes in genetic characteristics of tumors through the repeat testing process.
- MRD, risk factors of hematologic malignancy recurrence
-
The MRD indicates a small number of malignant cells remaining after or during treatment. These are used in follow-up observation particularly on hematologic malignancy diseases such as leukemia and lymphoma to monitor the reaction to a certain treatment or to predict the risk of recurrence.
The usefulness of ctDNA (circulating tumor DNA)
Blood contains cell-free DNA(cfDNA) and short DNA fragments from cells, and among them, cfDNA from tumor cells is called circulating tumor DNA(ctDNA).
- Non-invasive method
-
Since ctDNA exists in body fluids, the risk of complications is lower than in the case of tissue biopsy.
- Comprehensive information on cancer tissues
-
Cancer can be generated due to various variations in tumor tissues. While tissue biopsy can be confirmed information only on a local spot tumor, ctDNA contains broad-range information on cancer tissue.
- Convenient and prompt collection of specimen
-
A continuous test is crucial if the test is to confirm the prognosis/prediction, monitoring, and recurrence after the treatment. Only blood drawing is needed for the non-invasive use of ctDNA.
- Detection of small quantity of cancer cells
-
If a small quantity of tumor tissue via tissue biopsy in the early stage or during the treatment is unable to be detected, the ctDNA non-invasive test can be able to detect.
ctDNA core technology of NGeneBio
We are developing the core technology in the entire process from ctDNA extraction to sequencing data analysis.
-
ctDNA extraction
ctDNA in
Blood -

ctDNA Prep
-
Library preparation
Library prep
(UMI) -

Target hyb &
Capture -
Final
Amplification -
Analysis

Next Generation
Sequencing -
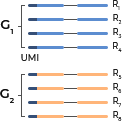
UMI Grouping
-

NGS Data Analysis &
Reports
- Minimization of sequencing error through UMI-technology
-
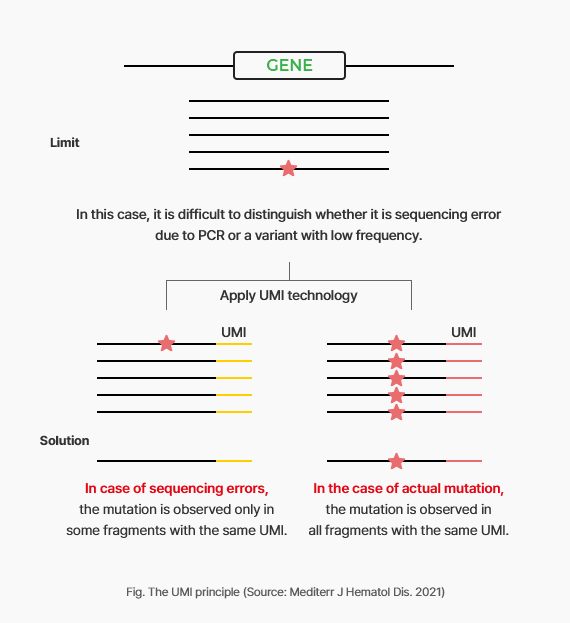
In the process of amplifying and sequencing ctDNA, which is 0.001% in blood, incorrect sequencing data might be generated. In this case, it is difficult to distinguish whether the variants are true positive mutations or false that occurred during the sequencing process.
In order to correctly identify variants we applied UMI (Unique Molecular Identifier) by amplifying ctDNA after attaching a tag to it and can distinguish actual mutation or not.
With the application of UMI technology, it is possible to accurately detect mutations of 0.5% or less with high sensitivity.
- Building a database for noise removal
-
We are building a database of ctDNA-specific false-positive mutations that exist at a frequency of less than 1% and minor mutations that are not cancer cells but may occur in hematopoietic stem cells depending on aging and health conditions. Based on this database, we are establishing a noise-filtering technology that removes errors.
Diagnosis for Minimal residual disease (MRD)
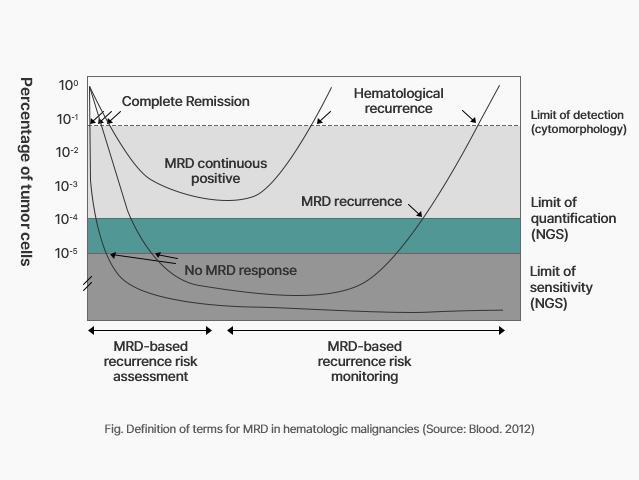
Recently, the importance of measuring ‘minimal residual disease (MRD)’, factors of cancer recurrence, is growing more than
Complete Remission (CR)* in the treatment of hematologic malignancy.
Previously, in order to evaluate whether or not complete remission* was achieved in hematologic cancer, morphological bone marrow reading was used to check whether cancer cells were reduced to less than 5%, but there is a limit to detecting minimal residual cancer cells invisible. *Complete remission : A state in which symptoms or lesions of the disease have been removed
If residual cancer cells are identified, it can also be interpreted as meaning that cancer treatment has not been effective or that cancer cells have become resistant to treatment drugs.
Advantages of NGS-based MRD testing
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend MRD diagnosis before bone marrow transplantation after completion of induction chemotherapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia.
The ELN (European LeukemiaNet) guidelines recommend MRD follow-up observation and monitoring to assess the risk of recurrence after the remission of acute myeloid leukemia.
Existing MRD observation methods such as flow cytometry or capillary electrophoresis could identify 1 tumor cell out of 100 or 1,000, but the NGS-based test method can identify tumor cells present at a low rate, such as 1 tumor cell out of 100,000. The NGS-based test has excellent MRD detection performance with high sensitivity.
Roadmap for development of liquid biopsy
-
ctDNA : Solid cancer
Set-up UMI technology
MRD : Hematologic malignancies
Patent
-
ctDNA : Solid cancer
RUO
MRD : Hematologic malignancies
RUO
Analytical performance test
Clinical performance test
-
ctDNA : Solid cancer
Analytical performance test
Clinical performance test
MRD : Hematologic malignancies
New medical technology evaluation
Domestic LDT(Laboratory-developed test)
- 2022
- 2023
- 2024
Companion diagnostics
Companion diagnostics is a test that selects target patients for targeted therapy in advance.
Companion Diagnostics (CDx) is a molecular diagnostic test that predicts a patient's responsiveness to a specific drug treatment,
confirms the amplification and overexpression of a specific gene, or tests for biomarker gene mutations.
The necessity of companion diagnostics
The companion diagnostics test is essential for the safe and effective use of drugs in patients.
It helps doctors make decisions about the course of a patient's drug administration, including identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from a particular drug, monitoring drug response, and identifying patients at increased risk from certain medications.
In recent years, cases of obtaining approval along with targeted therapy are increasing by developing companion diagnostic medical devices and reagents from the development stage of new drugs such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Patient

Diagnostic test
- Chemotherapy
-

Prescription of an anticancer drug without diagnostic test
- Targeted therapy
-
Target gene identification through genetic testing
Diagnosis and prescription
Treatment
Uncertain efficacy
Efficient treatment
Companion diagnostics
- Providing customized treatment for patients
-
Disease prevention and treatment
Prognosis
Monitoring
Reducing treatment time and costs
Using NGeneBio's precise diagnosis panels and analysis software, we are conducting large-scale clinical studies with major cancer hospitals in Korea, and are cooperating with pharmaceutical companies to develop companion diagnostic kits.
Current status of companion diagnostics research
Participation in 'Epidemiological evaluation and clinical outcomes of HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer and germline BRCA1 and 2 pathogenic mutations in Korea' using ‘BRCAaccuTest™ PLUS’: a multi-institutional prospective study to investigate prevalence & clinical outcomes' (~22')
Participation in ‘Randomized open-label phase 2 clinical trial of talazoparib versus talazoparib + atezolizumab after endocrine therapy with palbociclib in patients with premenopausal HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer with a homologous recombination defect’ using ‘SOLIDaccuTest™’ (~24’)
Participation in ‘Molecular epidemiology of germline mutations in Korean patients with metastatic prostate cancer’ using ‘SOLIDaccuTest™’ (~22’)
Participation in ‘A multicenter open-label phase 1b clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of TASO (TGF-β2 targeting anti-sense oligonucleotide)-001 as combination therapy with recombinant Interleukin-2 (Aldesleukin) in patients with advanced or metastatic solid cancer’ using ‘SOLIDaccuTest™’ (~23’)
Participation in ‘Phase 1a/1b published and multicenter clinical trial on safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of PHI-101 in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia (AML)’ suing ‘HEMEaccuTest™’ (~24')
Current status of FDA-approved companion diagnostics drugs
related to NGS diagnostic products
| NGeneBIO | INDICATIONS | BIOMARKERS |
FDA CDx APPROVED TERAPHY |
|---|---|---|---|
| ONCOaccuPanel™ | Solid tumors |
Genetic mutations - SNV, INDEL, CNV - SV(Fusion) - TMB, MSI |
Tagrisso Alecensa, Xalkori Kytruda |
| BRCAaccuTest™ PLUS |
Breast cancer Ovarian cancer |
BRCA1, BRCA2 genetic mutations |
Lynparza, Talzenna, Rubraca |
| HEMEaccuTest™ | Hematologic tumors |
Genetic mutations - SNV, INDEL - SV(Fusion) |
Tibsovo, Rydapt, Xospata, Venclexta |
| SOLIDaccuTest™ | Solid tumors |
Genetic mutations SNV, INDEL NTRK1, NTRK2, NTRK3 rearrangement SV (fusion) |
Avastin Rozlytrek, Vitrakvi |
| SOLIDaccuTest™ HRD | Solid tumors |
BRCA1, BRCA2 & HRD relevant gene mutations |
Lynparza, Jejula, Talzenna, Rubraca |
| HLAaccuTest™ | Uveal Melanom |
HLA-A*02:01 |
Kimmtrak |
Research Status
Samsung Medical Center (and 13 other major hospitals in Korea)
Asan Medical Center (and 12 other major hospitals in Korea)
New drug development
Workflow
Sample collection
- · Clinical trial institution
- · FFPE tissue
- · Peripheral blood,etc.

Sample delivery
- · Transportation company
- · Monitoring of temperature during delivery


NGS test

Issuance of a report
- · Specimen delivery and inspection
- · Execution of the NGS test
- · genetic variations anaylsis NGeneAnalySys
- · Test results
- · Issuance of the results report
For the safe and effective use of drugs, we collaborate with clinical trial institutions (hospitals) to conduct NGS tests using patient samples, analyze the results, and issue result reports.
Medical staff providing personalized medical (prevention, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis) services